The Next Generation NCLEX (NGN), effective from April 2023 for RN and LPN/LVN candidates, introduces changes to address the growing complexity of patient care, advancements in healthcare, and the need for safe clinical decision-making. It aims to improve new nursing graduates' ability to make safe clinical judgments by emphasizing clinical judgment as a core skill.
Key Changes from the Previous NCLEX to NGN:
Adaptive Test Format with Fewer Items:
- The NGN maintains the adaptive test format but with a reduced number of items. Candidates will answer between 85 and 150 items, including 15 pretest (unscored) items.
Case Studies:
- Each candidate will face at least three Unfolding Case Studies, each consisting of six test items (18 items in total). These case studies are presented in a medical record format and assess the ability to think critically and make safe clinical decisions across different phases of patient care. Additionally, some candidates may also encounter Stand-Alone Items.
New NGN Item Types:
- The NGN introduces new item types, which include questions in unfolding cases and stand-alone items, as well as highlight, cloze, matrix, bow-tie, drag and drop, and extended multiple response items.
Scoring Differences:
- NGN items will be scored using partial credit with three different scoring rules: the 0/1 scoring rule, the +/- scoring rule, and the rationale scoring rule.
Purpose of the Next Generation NCLEX (NGN)
The main goal of the NGN is to ask questions that more accurately assess a candidate's clinical judgment.
In 2013-2014, the NCSBN conducted the NCSBN Strategic Practice Analysis, which examined the knowledge and skills necessary for nursing practice. This analysis, along with supporting research, found that the minimum required knowledge and skills for nurses are increasing.
With the advancement of technology and the rising complexity of patient conditions, healthcare is becoming more challenging, leading to a higher risk of errors from poor clinical decision-making by nurses.
This need to improve the assessment of clinical decision-making skills is the driving force behind the NGN.
The National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM)
The NCJMM is a framework that outlines the steps nurses must take to address client needs effectively. It starts with recognizing cues indicating a problem and follows through a decision-making process to take action and evaluate the client’s response. The model enhances the traditional nursing process by offering a more detailed assessment of the cognitive processes involved in clinical judgment and the context of these decisions.
Clinical Judgment in the NCLEX-RN Test Plan
Clinical judgment is a crucial element of the NCLEX-RN Test Plan, reflecting the increasing complexity and demands of nursing practice. Nurses must engage in a continuous, multi-step process, using their nursing knowledge to observe and assess situations, identify client concerns, and develop evidence-based solutions to ensure safe patient care. Clinical judgment questions appear in Unfolding Case Studies or individual Stand-Alone Items, with case studies covering each step of clinical judgment. The six cognitive skills involved in clinical judgment are:
Recognize Cues: "What matters most?"
- Identifying relevant information from various sources like medical history, lab results, and vital signs.
Analyze Cues: "What could it mean?"
- Organizing and interpreting recognized cues in relation to the client’s clinical presentation.
Prioritize Hypotheses: "Where do I start?"
- Evaluating and ranking hypotheses based on urgency, likelihood, risk, difficulty, and time constraints.
Generate Solutions: "What can I do?"
- Defining expected outcomes and creating interventions aligned with these outcomes based on hypotheses.
Take Action: "What will I do?"
- Implementing the highest-priority solutions identified.
Evaluate Outcomes: "Did it help?"
- Comparing observed outcomes with expected outcomes to determine the effectiveness of interventions.
Unlike the traditional nursing process (ADPIE), the NCSBN emphasizes the AAPIE approach (assessment, analysis, planning, intervention, evaluation). The NGN does not test for nursing diagnoses, as they are not considered a universal language in healthcare. Instead, students must use their knowledge of pathophysiology to analyze client assessments and correlate them with common conditions in healthcare settings.
Sample NGN Test Question
In this case study, you will answer 6 Next Generation NCLEX style questions. Click the Next arrow at the bottom of the screen to advance to the next question. You must answer each question before advancing to the next question. Backtracking is not allowed.
Case Study Question 4 of 6
Case Study Question 6 of 6
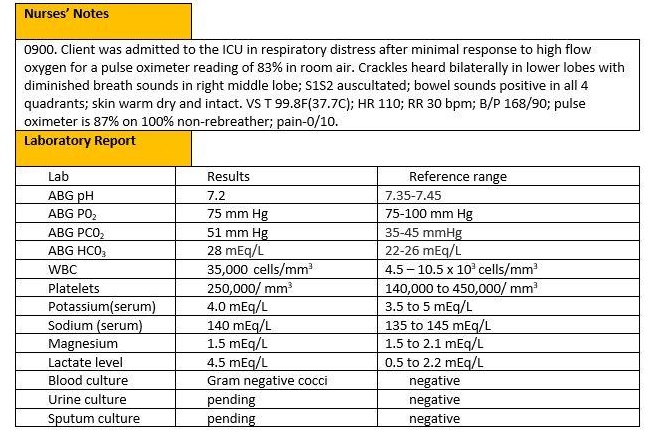
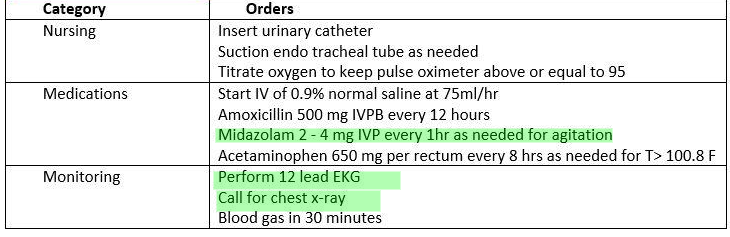
4. Sedation is needed to control agitation in an intubated patient. Repeat xray is done to assess depth of the tube and document tube placement. Suctioning is done as needed (PRN). Amiodarone is not indicated unless patient has a refractory V-tach. Antibiotics are indicated for the pneumonia which is the cause of the patient's respiratory failure. Patient will be positioned with head elevated between 15 to 45 degrees to allow lung expansion. EKG is indicated in all critical patients.
5. The 3 orders you will carry out first are chest xray for placement, midazolam for restlessness, and an EKG. Although the antibiotic is needed for pneumonia, it was ordered at a specific time as well as blood gas in 30 mins. Suctioning, and acetaminophen are ordered as needed. When answering questions looking for interventions to implement first, the PRN ones are not correct unless the scenario states that the indications for the PRN orders are present, in this case restlessness. The patient's oxygen saturation is at 96% so there's no need to titrate it at this time. The rest of the orders can be done later on.















.png)
No comments:
Post a Comment